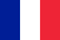
Osteocartilage degeneration is a disease in which degenerative nutritional changes are diagnosed in the cartilage tissue of the spine, accompanied by structural and dysfunction of the intervertebral disc. Osteochondrosis in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae are distinguished according to the location of the damaged tissue.

What is osteochondrosis?
Osteocartilage degeneration is a disease of the spine, in which degenerative and malnutritional lesions of the intervertebral disc occur. With the development of osteocartilage degeneration, degenerative disease lesions are suitable for vertebral tissue.
It is shown that the main characteristics of osteochondral toxin development are pain, progression, pain in the neck, back, and lower back areas "receiving" to the hands, chest, shoulders, shoulders, above the thighs, etc. The negative dynamics of osteochondrosis, atrophy of muscle tissue, atrophy of muscle tissue, sensitivity to damage, and inhibition of inhibition, are inhibited and inhibited. Displacement. Without timely treatment, osteochondrosis develops to an incurable state.
Causes of osteochondrosis
The main factor in the development of osteochondrosis is the uneven load on the spine. The habit of carrying bags on one shoulder or one hand, incorrect sitting posture, dreaming on an overly soft mattress, high pillows, wearing incorrect anatomically, are common causes of improper load distribution.
Other risk factors include sedentary and long-term sedentary lifestyle of the musculoskeletal system, excessive weight, back injuries, lower limbs, flat feet and other diseases, and age-related degeneration processes in age-related changes in vertebrae supply.
In the causes of osteochondrosis, the following factors can also play a role:
- physical overvoltage of the body;
- Nervous emotional fatigue;
- Metabolic diseases, poisoning, gastrointestinal diseases to prevent complete nutritional assimilation;
- Especially professional risks work on vibration platforms;
- Genetic tendency;
- Violate posture when growing actively, scoliosis;
- Wear uncomfortable shoes (narrow, high heels);
- prolonged and/or routine dehydration;
- Diet under diet, secondary amine disease;
- Smoking;
- Pregnancy, especially multifold, is combined with an undeveloped instrument of muscle ligament (due to displacement of the body's center of gravity).
The development stage of osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis in disease dynamics passes through four stages:
- The first stage (degree) of osteochondrosis is characterized by the initial stage of pathology in the Pulpos nucleus of the intervertebral disc. Due to excessive loading, the dehydration process of the core (dehydration) begins, resulting in a reduction in the parameters of disk height and the occurrence of cracks in the fibrous annulus. Symptoms are usually not present at this stage, and a long stay in uncomfortable stat positions, active exercise, etc. may cause mild discomfort.
- In both stages, a decrease in disc height can lead to a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae and the sagging of the vertebrates and ligaments. This can lead to increased mobility of the vertebrae, and displacement or sliding of the intervertebral disc is dangerous. In the second stage of the disease, discomfort, pain occurs, especially certain types of load, movement, position;
- Osteochondrosis stage 3 (degree) is characterized by prolapse and protrusion of the intervertebral disc, which may be accompanied by arthritis development in subluxis and/or vertebral joints. During certain types of exercise, patients will feel stiff, underactive, tingling, and numbness in the limbs. At this stage, osteocartilage degeneration is clearly felt in the back, neck, lumbar section or coccyx according to the positioning of the affected intervertebral disc.
- During the 4 stages of osteochondrosis, the body attempts to adjust the consequences of excessive vertebrae movement and adapt to impaired spine function. Bone plants are formed at the contact site of the vertebrae, and new bones form, which grasp the vertebrae to fixation. However, in some cases, bone plants can cause nerve erosion and damage the vertebrae. Fibrohypertension begins with the disc and joints. In the absence of microorganisms and nerve root infringement, the symptoms of the disease subside.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis are discomfort and/or pain in the neck and back. The severity of the feeling and the presence of other symptoms depends on the stage of the disease. When the patient is examined and the tumor is collected, the expert makes an initial diagnosis assuming osteocartilage is present in the curvature of the spine observed in the transverse or longitudinal plane of the vertebrae. The pathology of the cervical and lumbar discs is more frequent than that of the degenerative and malnutritional changes in the sternum area.
The signs of osteocartilage degeneration that patients feel include a periodic or permanent back fatigue depending on the stage of the disease, pain. The pain can be positioned on the neck, back, chest, and shoulder straps, making the movement of upper limbs more complicated.
The clinical image of osteochondrosis depends to a large extent on the pathological positioning, the degree of process development, and the individual characteristics of the patient. The pathology of intervertebral discs, displacement, herniation, and increased bone plants leads to various consequences. Most commonly, violations of normal blood circulation in tissues, clamping of nerve ends, dysfunction of spinal canals, edema, fibrosis of tissue and structure.
This consequence can be accompanied by many different symptoms, leading to a wrong diagnosis of the disease.
The most common and characteristic symptoms of osteochondrosis include:
- Pain in the back, neck, lower back, shoulder straps, rib areas;
- Discomfort, the stiffness of the body's movement in certain positions in the body, tilting, turning, and increasing muscle tension;
- The feeling of numbness in the upper and lower limbs;
- Muscle and joint discomfort, muscle spasms;
- Headache, dizziness, and increased fatigue;
- Heart pain;
- Violating the sensitivity of the hand;
- Muscle hypotension.
The symptoms of osteochondrosis depend on the location of the pathology:
- The bone cartilage of the cervical spine turns into bones, pain in the neck, hands, and shoulder straps, radiating to the shoulder area and shoulders, prevailing; headache, dizziness, "flies" or spots in front of the eyes, and noise in the ears are noticed;
- Due to damage to the chest and spine, pain is located on the chest, the inner surface of the shoulders, the area of the armpits, and discomfort and shortness of breath are possible;
- Osteochondrosis in the lumbar spine is manifested by pain in the lower back as the legs, upper thighs, or pelvic organs, which usually connect sexual dysfunction.
Surface symptoms – back fatigue, pain – not only indicate the presence of osteochondrosis, but also the addition of other diseases or other pathological processes and development of the disease that are not associated with disc malnutrition. Diagnosis of osteochondrosis can only be performed by experts, and self-assessment with such symptoms is unacceptable.
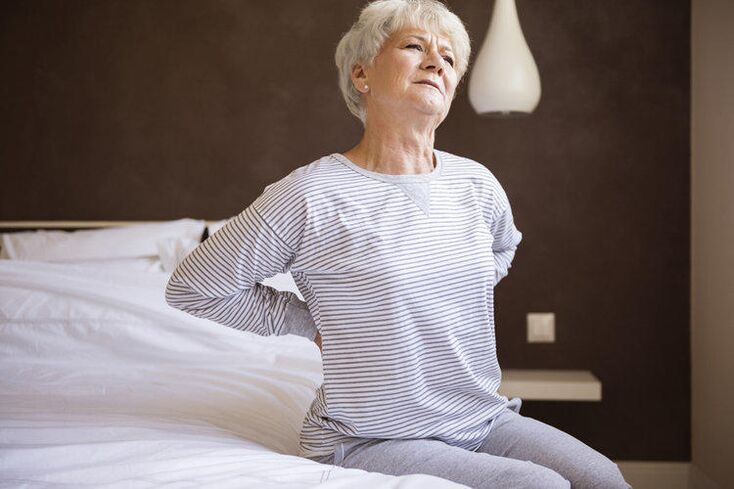
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
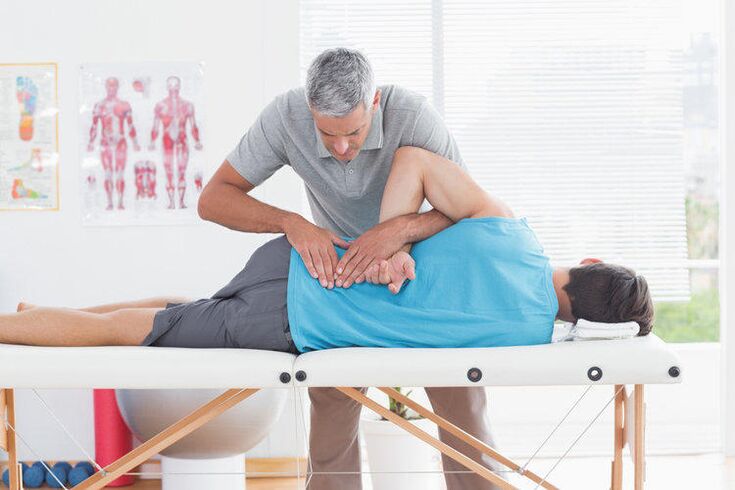
For diagnosis, instrument inspection methods were used:
- X-Spine department examination;
- Bone marrow science;
- Neurological sensitivity investigation, reflex.
Other methods prescribed for differentiation and clarification of diagnosis, pathological stages include:
- Computed tomography (CT) of the spine;
- nuclear magnetic resonance (JAMR);
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Treatment direction for osteochondrosis
Treatment is based on a comprehensive approach, based on stage, intensive care for 1 to 3 months and 1 year of support measures to consolidate outcomes and prevent recurrence.
Osteochondrosis was performed in both directions depending on the degree of osteochondrosis and the health of the patient. Conservative treatment of the disease involves taking medication and performing a series of exercises. In any case, surgical treatment is hardly the preferred method and the progress of the disease has been prescribed in the context of long-term conservative therapy without positive dynamics.
In addition to medical treatments, general recommendations for osteochondrosis must be followed: observe diet and take measures required for recovery.
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis
Conservative treatment aims to prevent pain syndrome, normalize spinal function and prevent negative changes
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis includes the following types of treatments:
- Drug therapy. Drugs for osteochondrosis are used to stop pain syndrome, inflammatory processes in tissues and normalize the body's metabolic processes. Using obvious pain syndromes, it is recommended to block the nerve ends, which also leads to a reduced severity of muscle tone syndrome. The following types of blockades are distinguished: blockade of trigger points, intra-bone, facet, parafur, epidural;
- Physical therapy. During recovery, physical therapy procedures are also used to help reduce pain and increase the effect of the medication. The most common uses of ultrasonic waves, magnetic fields, low-frequency currents, laser rays, etc.
- Physical therapy exercise (exercise therapy) and exercise therapy methods. The fragrance complex with regular and correctly performed helps to correct posture, strengthen muscle corsets, ligament instruments, normalize muscle function, reduce compression of nerve fibers, and help prevent complications of osteocartilage. The methods of exercise therapy and exercise therapy are designed to normalize the metabolic process, restore the entire nutrition of the intervertebral disc, restore the arrangement of vertebrae and intervertebral discs, and evenly distributed loads in the musculoskeletal skeletal system;
- massage. Manual massage techniques are used to improve tissue, reduce blood supply to muscle cramps and fixtures, and generally improve blood circulation. In addition to the listed effects, hydrates, as the direction of therapeutic activity, also contribute to the normalization of the body's nervous system.
- Manual therapy. Manual treatments are selected separately. The influence on the body's musculoskeletal system's perspective can help improve blood circulation, lymph circulation, improve metabolism, promote musculoskeletal system mobility, enhance the immune system, and be used as a means to prevent complications of osteochondral bone complications;
- Treatment with special equipment for spinal traction methods (traction force). The purpose of the manipulation is to increase the disc space to normal parameters and correct structures that violate the spine.
Prevent osteochondral disease

The main reasons for osteocartilage degeneration are connected without attentional needs, malnutrition, and excessive load in the body. To prevent the onset of pathological changes in the spinal column and limit the dynamics of existing osteocartilage, it is recommended to adhere to general principles of a healthy lifestyle:
- Unless the possibility of dynamics: moderate exercise: charging, running, swimming, cycling, snowboarding, gymnastics, contactless type struggle types, etc. ;
- When work or other forms of activity are associated with static locations related to long-term stays, it is necessary to rest every 45 minutes to restore blood circulation. If necessary, after sitting for a long time, you should choose a right chair, make sure your spine supports, monitor to meet the standards of the hands on the table, legs on the floor or on special brackets, habitual posture (even back, relaxed shoulder);
- For nighttime sleep, it is necessary to choose elasticity with flat surfaces, better orthopedic mattresses, and avoid high or too flat pillows;
- If necessary, lift and/or wear heavy objects to avoid assholes, increase severity from semi-refined positions, use special belts that support the lower back;
- The right shoe choice in orthopedics: If the corresponding foot straps are width and no high heels, timely replacement will help reduce the burden on the spine, which is especially important for women during childbirth. In summer, don't ignore the ability to walk barefoot on uneven surfaces, which will strengthen the muscles of the feet and reduce tension in the musculoskeletal system.
- The right diet, drinking pattern helps overall health and helps maintain metabolism normally;
- Because of the tendency to increase emotions, anxiety responds to muscle spasms to stress, it is worth studying relaxation methods.